Updates
Discoveries
Organizations
Top Health Organizations that are doing research which will change the way we will understand our psychology.
Psyarxiv
BioRxiv
MedRxiv
PubMed Central
Frontiers
PLOS
Journal of Neuroscience
eNeuro
Biological Psychology
How biological processes influence behaviors, thoughts, and emotions
Hemisphere deconnection and unity in conscious awareness (1968)
The Effects of an Enriched Environment on the Histology of the Rat Cerebral Cortex (1964)
Experience and brain development (1987)
Brain abnormalities in murderers indicated by positron emission tomography (1997)
Neuroscience: Breaking down scientific barriers to the study of brain and mind (2000)
Fear memories require protein synthesis in the amygdala for reconsolidation after retrieval (2000)
Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function. (2010)
Brain Images Just Got 64 Million Times Sharper (2023)
Cognitive Psychology
How mental processes influence perceiving, learning, thinking, and remembering
Newell and Simon's Logic Theorist: Historical Background and Impact on Cognitive Modeling (1956)
Visual perception of biological motion and a model for its analysis (1973)
Neon Color Spreading: A Review (1997)
A new visual illusion of relative motion (2000)
The Influences of Category Learning on Perceptual Reconstructions (2004)
Perception of illusory contours enhanced in motion (2004)
White's effect: Removing the junctions but preserving the strength of the illusion (2005)
THE BASICS OF LINE MOIRÉ PATTERNS AND OPTICAL SPEEDUP (2007)
Mindfulness meditation improves cognition: Evidence of brief mental training (2010)
The Ōuchi-Spillmann Illusion Revisited (2013)
Evolving Ambiguous Images (2015)
The Cafe Wall Illusion: Local and Global Perception from multiple scale to multiscale (2017)
Curvature Blindness Illusion (2017)
Evolution of Impossible Objects (2018)
Clinical Psychology
Diagnosing and treating mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders
Client Centered Therapy (1951)
Cognitive Therapy of Depression (1979)
Cognitive-behavioral treatment of borderline personality disorder (1993)
Clinician’s Guide to Mind Over Mood (1995)
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy: An experiential approach to behavior change (1999)
Positive psychology: An introduction (2000)
Book summary: Unlocking the Emotional Brain (2019)
Analysis of Psilocybin-Assisted Therapy in Medicine: A Narrative Review (2022)
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide–Assisted Therapy (2023)
Developmental Psychology
How humans change over the course of their life
The Construction of Reality in the Child (1954)
Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models (1961)
Attachment and Loss, Volume I: Attachment (1969)
The claim to moral adequacy of a highest stage of moral judgmen (1973)
The Psychology of Sex Differences (1974)
A C. elegans mutant that lives twice as long as wild type (1993)
Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene (2003)
Development of the adolescent brain: implications for executive function and social cognition (2006)
Case report: High prenatal bisphenol A exposure and infant neonatal neurobehavior (2016)
Lifespan: Why We Age―and Why We Don't Have To (2019)
Social Psychology
How our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the presence of others
Effects of group pressure upon the modification and distortion of judgments (1951)
A Theory of Cognitive Dissonance (1957)
Behavioral study of obedience (1963)
Social categorization and intergroup behaviour (1971)
The Stanford Prison Experiment: A Simulation Study of the Psychology of Imprisonment (1973)
The spread of true and false news online (2018)
On the Origins of Memes by Means of Fringe Web Communities (2018)
Social Media and Political Dysfunction: A Collaborative Review (2021)
Behavioral Psychology
How our observable actions affect the way we act and think
Conditioned emotional reactions (1920)
Schedules of reinforcement (1957)
Failure to escape traumatic shock (1967)
Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change (1977)
A new look at habits and the habit-goal interface (2007)
A Behavior Model for Persuasive Design (2009)
How are habits formed: Modelling habit formation in the real world (2010)
The Power of Habit: Why We Do What We Do in Life and Business (2012)
The One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary Results (2013)
Atomic Habits: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad Ones (2018)
Disorders

Disorders should be a spectrum not a "on or off" switch or "you have it or you don't" kind of thing. I do not believe in saying "this person has (insert this disorder)" instead "This person has displayed more traits belonging to (insert this disorder)." All identities are illusions anyway.
We should think of disorders as a percentage not something to just label people. I say this because humans are deeply flawed. All of us are guilty in behaving in ways that are illustrated by all these disorders due to our genetic code that is printed with behavior geared towards surviving and reproducing.
The causes, treatment, and symptoms of psychological disorders are extremely diverse and multifaceted. This list meant to merely introduce people to the idea of psychological disorders NOT to diagnose or treat them. Symptoms often fit multiple disorders. If you feel that you might have any of the disorders listed, then a natural course of action is to try out different forms of therapies and see what works for you.
Emotionally immaturity is at large when it comes to younger people (especially in high school or in university). Lots of people want relationships and friendships but a lot of people do not necessarily know how to deal with those people and they don't even know how to deal with themselves. Everyone's brain is still developing and its hard transitioning to an adult.
A lot of psychological disorders happen through a child's relationship with their parents. Reason being is when a child is being cared for their brains are still developing. If it's needs are not met by its Father or Mother then psychological emotional issues often take root. Parents are extremely important for the successful development of children. Manipulative Parents who have unresolved emotional issues will breed the same behavior in their kids. Never Forget It.
People who have more disorder traits do not necessarily display all the symptoms and younger people especially are going to make mistakes and do dumb things because they are learning. We also live in a society that rewards manipulative behavior (money, success, relationships, sex, etc). Sometimes in order to be successful you have to be a little manipulative.
Hopefully in the future we transition into a society where people aren't forced to be manipulative in order to be valued by other people. Feel free to assess yourself and your behaviors. This will make sure that you know them and hopefully become a less manipulative person in the future.
Table of contents
Depressive Disorder
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
Derealization Disorder
Schizophrenia
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)
Anxiety Disorder
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Dependent Personality Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Psychological Based Shows
Depressive Disorder

Definition
Persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest in activities, and a range of emotional and physical problems, significantly impairing a person's ability to function in daily life.
Symptoms
1. Persistent Emptiness, Sadness, or Anxiousness
2. No Interest or Pleasure In Anything
- Persistent sad, anxious, or "empty" mood
- Not caring about anything
- Nothing matters anymore
- Not wanting anything
- Not wanting anybody
- Feelings of hopelessness, or pessimism
- Irritability
- Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, or helplessness
- Loss of interest or pleasure in hobbies and activities
- Decreased energy or fatigue
- Moving or talking more slowly
- Feeling restless or having trouble sitting still
- Difficulty concentrating, remembering, or making decisions
- Difficulty sleeping, early-morning awakening, or oversleeping
- Appetite and/or weight changes
- Thoughts of death suicide
- Aches or pains, headaches, cramps, or digestive problems without a clear physical cause and/or that do not ease even with treatment
Fictional Cases
Shinji from Neon Genesis Evangelion displays multiple signs of depression. This stems from his relationship with his father. He seeks validation and approval from his father and his father doesn't give it to him. This makes him feel worthless. Exteremly worthless. And this manifests itself in his difficulties in forming meaningful relationships. It's his deep-seated fear of rejection that makes it hard for him to emotionally relate to others since he can't relate to his father. And because he can't relate to his father, he can't even relate to himself.
During a conversaiton with Misato he says "I'm worthless. I'm not even sure I really exist." The more things get harder the more he runs away. At first people often assume he lacks confidence or self-esteem but in actuality its something far deeper. His entire identity and self-worth stribes from his relationship with his father. His mother is dead and he has a virtual nonexistent relationship with his father. These feelings get stronger the more stress he experiences.
Asuka adds to the fire. She wants him to be more confident. She senses his feelings of inadequacy and his difficulties in expressing himself which make her uncomfortable. So she often belittles Shinji and challenges Shinjii, but his way of handling conflict is retreating into himself, into his low self-esteem. This causes Asuka to belittle Shinjii even more.
Shinjii doesn't like this. He explains it to Misato and Misato explains: "She's mad because you're always worried about what other people think." But Shinjii can not resolve this. He can't resolve his low confidence because he can't resolve his relationship with his father. Later on, he is put into harder and harder situations and emotionally vomits his problems out. He cries out that he feels worthless and useless, how much he hates his father, and how nobody seems to care or understand.
And because this issue seems unresolvable he feels utterly worthless. Nothing matters. He doesn't want to pilot the evas. He doesn't want relationships or friendships anymore. He doesn't want to do anything.
Borderline Personality Disorder

Definition
Unstable moods, behavior, and relationships, often involving impulsivity, fear of abandonment, and difficulty in managing emotions and relationships
Symptoms
1. Intense, Unstable Relationships
2. Impulsive, Often Self-Destructive Behaviors
- Frantic efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment
- A pattern of intense and unstable relationships with family, friends, and loved ones, often swinging from extreme closeness and love (idealization) to extreme dislike or anger (devaluation)
- Distorted and unstable self-image or sense of self
- Impulsive and often dangerous behaviors, such as spending sprees, unsafe sex, substance abuse, reckless driving, and binge eating
- Recurring suicidal behaviors or threats or self-harming behavior, such as cutting
- Intense and highly changeable moods, with each episode lasting from a few hours to a few days
- Chronic feelings of emptiness
- Inappropriate, intense anger or problems controlling anger
- Having stress-related paranoid thoughts or severe dissociative symptoms
Fictional Cases
Asuka also from Neon Genesis Evangelion has a similar story to that of Shinji. Her mother killed herself and her father was too busy with other women for her to get support. Being a young child the only way to survive was to hide all vulnerabilites (all neediness) and develop defense mechanisms. The problem is she desperately wants emotion and love despite hiding her feelings for it. She has to hide her feelings for it because of the fear of vulnerability. The vulnerability that stemed from being a vulnerable child and not getting her needs met.
Asuka is drawn to strength and assertiveness. She tries to embody it because it's what made her able to hide her own vulnerabilites. Shinji lacks these traits which makes her uncomfortable so she projects her own insecurities onto him. This is because she of course is terrified of showing that she has these traits and perhaps because she senses some attraction for Shinjii. Her projection can be explained by the fact that she was never given her needs met.
Because Asuka never got her needs met she displays intense fear of abandonment. She also has frequent mood swings from enthusiastic and confident to angry and confrontational. She wants to desperately prove herself to others. Asuka struggles with her sense of self and self-worth. It's just like Shinjii but she tries to hide it instead of showing it. Her sense of self seems heavily dependent on her performance and the validation she receives from others. All this is a mask to hide her neediness. Her neediness coming from her unmet needs from her parents.
Later on, Asuka has a mental breakdown following a traumatic experience with the Angel. Arael exposes her deep-seated fears of being alone and unloved. The feelings that she was always trying to hide eventually came out.
Derealization Disorder

Definition
Persistent or recurrent feelings of detachment or unreality about one's surroundings, as if they are in a dream or distant
Symptoms
1. Persistent or Recurrent Feelings of Detachment
2. Experiences of Unreality or Detachment From Surroundings
- Feelings of being an outside observer of one's thoughts, feelings, body, or actions
- Experiencing the world around you as unreal, dreamlike, distant, or distorted
- A sense that what is happening is not real, even when aware that the perception is not accurate
- Feeling emotionally disconnected from people, as though they are separated by a glass wall
- Surroundings appear visually distorted, such as objects changing in size, shape, or color
- A sense of time moving unusually slowly or quickly
- Feeling a lack of control over your speech or movements
- Awareness that these experiences are not congruent with reality and are symptoms of a disorder
- Symptoms cause significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
- The disturbance is not better explained by another mental disorder, such as schizophrenia, panic disorder, major depressive disorder, or another dissociative disorder
Fictional Cases
Rei is a product of bioengineering, created using the genetic material of Yui Ikari, unaware of it. She frequently questions her own identity and existence. In one scene she says "Who am I? What am I? What is Rei Ayanami?" which reflects a uncertainty about her own place in the world. Because she is not connected to herself or her emotions she often acts emotionless, muted, and robotic. This makes it hard to connect with her or have conversations with her.
In the scene where Shinji asks Rei why she pilots the Eva, her response was, "Because I have nothing else," which reflect a sense of emptiness and a lack of personal attachment or purpose beyond her role as an Eva pilot. This shows a disconnection from a traditional sense of identity or personal desires.
Schizophrenia
Definition
Distortions in thinking, perception, emotions, language, sense of self, and behavior, often manifesting as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
Symptoms
1. Delusions
2. Hallucinations
- Hearing voices or sounds that aren't there (auditory hallucinations)
- Seeing things that aren't there (visual hallucinations)
- False beliefs that are not based in reality (delusions of persecution, grandeur, or reference)
- Disorganized thinking (evident in speech)
- Extremely disorganized or abnormal motor behavior, including catatonia
- Negative symptoms, such as diminished emotional expression or avolition (lack of motivation)
- Trouble focusing or paying attention
- Impaired ability to understand information and use it to make decisions
- Reduced speaking, even when required to interact
- Trouble with executive functions (planning, organizing)
- Apathy or lack of interest in daily activities
- Social withdrawal
- Inappropriate or blunted emotional responses
- Symptoms cause significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
- The disturbance is not better explained by another mental disorder, substance abuse, or a medical condition
Fictional Cases
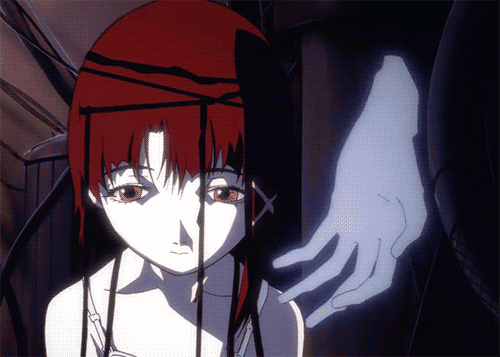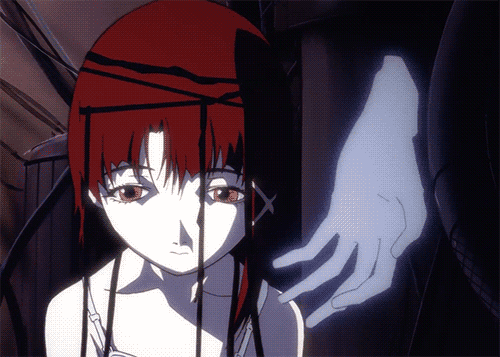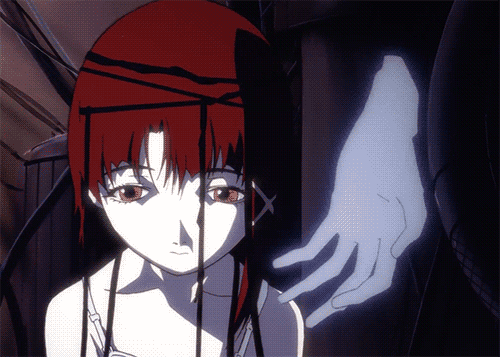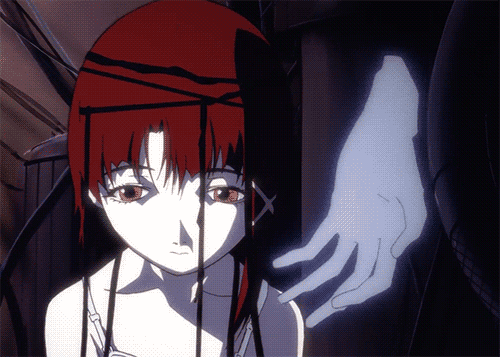
Lain from Serial Experiments sees a blured line separating the vision of reality and the digital world of the Wired. These experiences become more intense and disorienting, resembling hallucinatory experiences where she cannot distinguish between reality and her online existence.
Lain frequently questions her own reality. Whether certain experiences she has are real or not. She exhibits multiple signs of visual delusions which shows that she percieves a vastly different reality than her peers. Her confusion and hallucinations make it hard for her to communicate effectively with others. Her thought processes and conversations appear disjointed or illogical which make it hard for other people to understand or relate to her.
Because of this, Lain exhibits social withdrawal and a lack of emotional expression. She becomes increasingly isolated, diving deeper into her online persona. As Lain delves deeper into the Wired, she becomes increasingly paranoid about the entities and forces operating within it, as well as their impact on the real world.
As she dives deeper, Lain starts conversing with an entity she perceives as a god or creator. This voice significantly impacts Lain's thoughts and behaviors, guiding or influencing her actions. Lain hears and interacts with a voice or entity that others cannot perceive, indicative of experiencing a reality that is distinct from the consensus reality. When her friend Alice comes over she is unaware of this presence, highlighting a stark disconnect between Lain's perceived reality and the reality experienced by others around her. Lain is talking to an entity, a voice she clearly percieves while her friend can not percieve this entity.
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)

Definition
An inflated sense of self-importance, a deep need for excessive attention and admiration, and a lack of empathy for others.
It's possible to be narcissistic and not be a terrible person. If you use your narcissitic traits to create value to make society better and people better than are you truly narcissistic?
And a good amount of narcissism can be healthy for an individual. Our capaitalist society pretty much forces us to be manipulative in order to pursue our goals to create value. As long as you're doing it to make society and people better then the behavior is usually universally rewarded and praised.
Symptoms
1. Unable To Be Vulnerable
2. Lack Of Empathy
Manipulative people in general do not like to share their vulnerabilites at all (even little vulnerabilites). Remember if you are truly confident you are ok with being vulnerable. Also whenever they do create value it isn't because they genuinely care about others. It's mostly because all they really care about is themselves. And yeah, manipulative people attract manipulative people.
- Criticize you in a way that is not meant to help you but instead to tear you down
- Unable to take any good criticism (Unable to be Vulnerable)
- Needs to be seen as "perfect" (Unable to be Vulnerable)
- Unable to take ownership for their own problems (Unable to be Vulnerable)
- Mean nasty comments whenever possible (Humiliate) (Shame) (Tear Down) (Name-calling) (Projection) (Gas lighting) (Insults)
- Huge Social Media Addict (Frequent Gossip) (Frequent Misinformation) (Wanting Attention/Likes) (Everything is fake) (no posts that may show they are vulnerable or flawed or that may actually help people) (Useless Facebook and Instagram Posts that are all about them)
- Never apoologize (No accountability) (Nothing is ever their fault) (Unable to be vulnerable)
- No empathy when you're vulnerable (Unable to be vulnerable)
- Use your vulnerabilites so they can manipulate and control you (Unable to be vulnerable)
- Unable to show you aspects of their life (like friends or hobbies) (Unable to be vunlerable)
- To avoid taking any responsibility for you they will either act like they are more important than you or you're somehow a failure (Guilt Tripping) (Unable to be vulnerable)
- On and off Love Bombing in an attempt to control you
- Highly Externally Validated (Arrogance) (Obessed with Success and Making it) (Everyone MUST be aware of their success) (ALWAYS center of attention) (Speaks in terms of "I" instead of "you" and "we")
- Always act superior or more responsibile or just better than you in some way ("Put them in their place")
- Do not like seeing the success of others (Always must compete with you)
- Enjoy seeing others fail
- They try to control your life
- They want you to fix all their problems
- Frequent Lying
- Exaggerates Your Flaws
- Dissmive of your good qualities
- Praise you so they can tear you down later
Fictional Cases
Light Yagami from Death Note exhibits a grandiose sense of self-importance. He believes he is uniquely qualified to judge and eliminate those he deems morally unworthy. He refers to himself as the "god of the new world," which suggests his belief in his superiority over others. He frequently fantasizes about creating a utopian world where he reigns supreme. He imagines a future where crime is eradicated through his actions, and he is revered and worshipped.
Light seeks and relishes the attention and fear that his alter-ego, "Kira," receives from the public and media. His need for admiration and recognition is a driving force behind his actions. He demonstrates a strong sense of entitlement, believing that he is above the law and moral codes that govern ordinary people. He feels entitled to pass judgment on others and decides who lives and who dies, without any legal or moral authority to do so.
Light manipulates and uses otheers for his benefit, showing a lack of empathy and a willingness to exploit people to achieve his goals. A clear example is his manipulation of Misa Amane, whom he uses for her Shinigami eyes and as an alibi, despite her genuine affection for him. He is willing to sacrifice anyone, including family and friends, for his ambitions. His emotional responses to the deaths and suffering of others are often shallow or nonexistent.
Anxiety Disorder

Definition
Persistent and excessive worry or fear about everyday situations, often accompanied by physical symptoms such as a rapid heartbeat, sweating, and feelings of stress or overwhelm
Symptoms
1. Excessive Worry or Fear
2. Physical Symptoms of Anxiety
- Feeling nervous, restless, or tense
- Having a sense of impending danger, panic, or doom
- Increased heart rate
- Rapid breathing (hyperventilation)
- Sweating
- Trembling
- Feeling weak or tired
- Trouble concentrating or thinking about anything other than the present worry
- Having trouble sleeping
- Experiencing gastrointestinal (GI) problems
- Having difficulty controlling worry
- Avoiding situations that trigger anxiety
- Symptoms cause significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
- The anxiety is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition
Fictional Cases
Shoya from A Silent Voice becomes socially withdrawn after his bullying of Shoko Nishimiya, a deaf girl, in elementary school leads to him being ostracized by his peers. He avoids eye contact and interaction with his classmates, indicative of social anxiety and a deep-seated fear of judgment or rejection.
Shoya's anxiety and social withdrawal is represented through 'X' marks on the faces of those around him, symbolizing his inability to look at or connect with them. He exhibits low self-esteem and is plagued by guilt and self-blame for his past actions. His negative self-perception contributes to his anxiety, particularly in social situations, as he fears further judgment and alienation.
Shoya experiences physical symptoms of anxiety, such as sweating, nervousness, and a racing heart, especially when faced with social interactions or when thinking about his past. He often ruminates over his past actions and their consequences. He is haunted by memories of bullying Shoko and the social isolation that followed, leading to persistent, distressing thoughts that are common in anxiety disorders. Even though Shoya suffers from anxiety and fear of rejection, he still tries to overcome his anxiety and reconnect with others.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder

Definition
flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the event.
Symptoms
1. Intrusive Memories of the Traumatic Event
2. Avoidance of Reminders of the Trauma
- Recurrent, unwanted distressing memories of the traumatic event
- Reliving the traumatic event as if it were happening again (flashbacks)
- Upsetting dreams or nightmares about the traumatic event
- Severe emotional distress or physical reactions to something that reminds you of the traumatic event
- Trying to avoid thinking or talking about the traumatic event
- Avoiding places, activities, or people that remind you of the traumatic event
- Negative changes in thinking and mood
- Feelings of hopelessness about the future
- Memory problems, including not remembering important aspects of the traumatic event
- Difficulty maintaining close relationships
- Feeling detached from family and friends
- Lack of interest in activities you once enjoyed
- Difficulty experiencing positive emotions
- Feeling emotionally numb
- Changes in physical and emotional reactions
- Being easily startled or frightened
- Always being on guard for danger
- Self-destructive behavior, such as drinking too much or driving too fast
- Trouble sleeping
- Trouble concentrating
- Irritability, angry outbursts, or aggressive behavior
- Overwhelming guilt or shame
- Symptoms cause significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
- The disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition
Fictional Cases
Okabe repeatedly witnesses the death of his friend Mayuri, which deeply traumatizes him. He relives this event numerous times due to his time-traveling attempts to save her. He shows signs of physical distress, such as sweating and shaking, when reminded of his traumatic experiences.
Okabe tries to avoid discussing or dealing with the events he's witnessed. He often appears on edge and has a heightened startle response, especially when something reminds him of the traumatic events he's experienced. He is in a state of increased anxiety and being constantly 'on guard'.
Okabe demonstrates feelings of hopelessness, memory problems, and a negative perception of himself and the world around him. He blames himself for the events that occur and struggles with feelings of guilt and shame. He becomes more isolated and has difficulty expressing his emotions, which affects his interactions with those close to him.
Dependent Personality Disorder

Definition
Pervasive and excessive need to be taken care of, leading to submissive and clinging behavior and fears of separation.
Symptoms
1. Excessive Dependency on Others
2. Difficulty Making Everyday Decisions Without Reassurance
- A need for others to assume responsibility for most major areas of their life
- Difficulty expressing disagreement with others because of fear of loss of support or approval
- Difficulty initiating projects or doing things on their own
- Going to excessive lengths to obtain nurturance and support from others
- Feeling uncomfortable or helpless when alone because of exaggerated fears of being unable to care for themselves
- Urgently seeking another relationship as a source of care and support when a close relationship ends
- Unrealistically preoccupied with fears of being left to take care of themselves
- Difficulty making everyday decisions without an excessive amount of advice and reassurance from others
- Symptoms cause significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
- The behavior is not better explained by another mental disorder, such as a mood disorder, anxiety disorder, or a personality disorder like borderline or avoidant personality disorder
Fictional Cases
Misa's entire life and actions revolve around Light. She exhibits an intense and submissive attachment to him, often disregarding her own well-being for his sake. Her identity and decisions become heavily dependent on Light's approval and presence. Misa frequently expresses her undying loyalty to Light, saying things like, "I would do anything for you, Light," or "I can't live without you."
Misa demonstrates a profound fear of being abandoned or separated from Light. She goes to great lengths to maintain her relationship with him, even in the face of potential danger or moral compromise. She often expresses fear of losing Light's affection, saying things like, "Don't leave me," or "What would I do if you weren't here?"
Misa exhibits a willingness to submit to Light's will and demands, often without regard for her own opinions or safety. She rarely challenges Light's decisions and views his approval as essential to her self-worth. Misa might say, "Just tell me what to do, Light," or "I'll follow your orders, no matter what they are."
Misa struggles to make decisions on her own and relies heavily on Light to guide and direct her actions, especially regarding the use of her Death Note and her role in Light's plans. n moments of decision-making, she often defers to Light, saying things like, "What should I do next, Light?" or "I'll leave it up to you."
Autism Spectrum Disorder

Definition
Difficulties with social interaction and communication, and by restricted and repetitive behavior, interests, or activities
Symptoms
1. Challenges in Social Interaction
2. Restricted, Repetitive Patterns of Behavior, Interests, or Activities
- Difficulty in developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships
- Lack of social or emotional reciprocity
- Nonverbal communication issues, such as trouble understanding body language or maintaining eye contact
- Delayed speech and language skills or, in some cases, not speaking at all
- Repeating words or phrases over and over (echolalia)
- Giving unrelated answers to questions
- Getting upset by minor changes in routine or surroundings
- Having obsessive interests
- Flapping their hands, rocking their body, or spinning in circles
- Unusual reactions to the way things sound, smell, taste, look, or feel
- Symptoms cause significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
- The disturbance is not better explained by another mental disorder, such as intellectual disability or global developmental delay
Fictional Cases
L often appears socially awkward and has difficulty forming conventional social relationships. He is seen as a loner and does not engage much with others unless necessary for his investigations. interactions are usually brief, direct, and focused primarily on his detective work rather than social pleasantries
L has unique mannerisms, such as his distinctive way of sitting, eating sweets compulsively, and avoiding direct eye contact. His communication style is often blunt and straightforward. L speaks in a monotone voice and usually gets straight to the point in conversations, focusing more on logic and facts rather than emotions or social cues.
L is intensely focused on solving cases and displays a high level of intelligence and analytical thinking. He can be obsessive in his pursuit of a case, often at the expense of social interactions and self-care. He often talks extensively about the details of the cases he is working on, showcasing his deep focus and expertise.
L seems to have a specific routine, especially in his working environment, and he prefers to have control over his surroundings. Although not often explicitly stated in his dialogue, his actions, such as always using a specific type of laptop and having a controlled workspace, reflect this trait.
Psychological Based Shows
Therapies

Therapy is highly diverse, subjective, and variable. What might work for one person might work for an entire different person regardless of the disorder. I do not believe in prescribing the same drug or therapist for each individual disorder. Everyone is different so you will have to find what works for you.
We should not treat therapy as some medicine or drug but instead treat it as something you do that makes you happy. Something that gives you purpose or meaning or value in life. We should think of all our hobbies as therapies we use to cope with life. We should treat all our hobbies and habits as therapies that make life worth living.
Even though life is hard it's worth living if you manage to create the right lifestyle for yourself to overcome life's challenges. This is pretty much the realization that most philosophers have come to: Nietzsche, Kierkegaard, Sartre, Camus - you name it. It's also pretty much the life lesson/theme in all the most famous stories, movies, books, shows etc. Even though life can appear meaningless, individuals can create their own meaning and value through their lifestyle choices. The problem lies in what lifestyle is correct for you. Choosing the correct lifestyle is hard, but practicing the right therapies makes it easier.
Hopefully in the future we transition into a society where people can choose to do things that they truly enjoy. If people could do what they truly enjoy they would have less psychological issues. Feel free to try any therapy that you think will work for you. If you're able to build a lifestyle with therapies that help you then you will live a much more emotionally fulfilling life. In other words, continue to do what you truly enjoy, try not to hurt others, and keep working towards being the best version of yourself. ♥
Table of contents
Integrative Therapy
Journal/Question Based
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Psychodynamic Therapy
Humanistic Therapy
Interpersonal Therapy (IPT)
Psychoanalysis
Attachment-Based Therapy
Gestalt Therapy
Existential Therapy
Group Therapy
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT)
Creation Based
Music Therapy
Drama Therapy
Narrative Therapy
Art Therapy
Movement Therapy
Play Therapy
Video Therapy
Meditation
Mindfulness Meditation
Loving-Kindness Meditation (Metta)
Body Scan Meditation
Mantra Meditation (TM)
Yoga Meditation
Zen Meditation
Vipassana Meditation
Hobby Based
Animal-Assisted Therapy
Wilderness Therapy
Growing-Based Therapies
Video Game Therapy
Puzzle-Based Therapy
Engineered Based
Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy
Biofeedback
Hypnotherapy
Resources
Integrative Therapy
Integrating all these different therapies allows us to live a much more emotionally fullfilling life. Everyone already does this. Whether that be talking to people, listening to music, watching shows, etc. We all have different therapies in our lifestyle that help us cope with life. The question is whether we really like those therapies. Whether we can utilize better therapies to help us live better lives. Basically by integrating the right therapies correctly you stand a chance at creating the value you want and building the lifestyle you really want.
Steps
1. Identify The Problem
2. Explain The Problem
3. Find Solutions For The Problem
4. Make More People Aware The Problem Exists And Possible Solutions To The Problem
Therapies allow you to do this. Choose which one fits for you and implement it in your lifestyle.
Journal/Question
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Altering negative thoughts and behaviors by replacing them with more positive, realistic ones.
Steps
1. Identify Your Thoughts
2. Analyze These Thoughts
3. Shift Your Perspective
4. Alter Your Actions
Steps Explained
First Identify the Negative thought. Negative thoughts come to people all the time. When they come to you just identify them.
Next Challenge the thought. Gather as much evidence, reasoning, and potential biases for the thought. Write as much out if you have to. Come out with multiple explanations for the thought, and against the thought. Then ask what can you do about it?
Then Reframe the thought. This reframing should be more balanced and realistic. The effectiveness of reframing depends significantly on how thoroughly and honestly you've challenged the initial negative thought. You have got to be honest with yourself.
Then Update your behaviors. Engage in behaviors that challenge those thoughts. Implement them in your lifestyle.
Finally continually Reflect and Upgrade your behaviors by Identifying, Challenging, Reframing, and Updating, thoughts, behaviors, and beliefs. We all already do this. The question is whether we do it well.
Psychodynamic Therapy
Explores past experiences and emotions to understand current behavior.
Steps
1. Reflect on Past Experiences
2. Understand Emotional Patterns
3. Connect Past with Present Behavior
Steps Explained
First Identify past habits, behaviors, thoughts, and beliefs to understand current beliefs, thoughts, and behaviors
Next look for Patterns in past habits, behaviors, thoughts, and beliefs that lead to current beliefs, thoughts, and behaviors
Then connect the Patterns in the past to the current Patterns in the present.
Then Update your Patterns in the present to change your current beliefs, thoughts, and behaviors
Finally continually Reflect and Upgrade your behaviors by Identifying past and current Patterns
Humanistic Therapy
Focuses on individual potential and self-actualization.
Steps
1. Self-Exploration
2. Recognize Strengths and Weaknesses
3. Personal Growth Development
Steps Explained
First Identify Your Feelings, Values, and Beliefs: What made you choose to be in the position you are in right now?
Next Identify Your Choices and Responsibilities: Is there something you can do? Something that can be done that only you have the power to do? Figure out what you need to do right now so you don't have any regrets later.
Embrace Self-Growth and Self-Acceptance: One you've accepted that something can be done then do it and embrace it.
Interpersonal Therapy
Addresses interpersonal issues to improve relationships and mood.
Steps
1. Identify Relationship Patterns
2. Improve Communication Skills
3. Resolve Interpersonal Conflicts
Steps Explained
First identify the Issue in the Relationship
Next identify your Role in the Relationship
Then understand the underlying patterns behind the Issue and Role in the Relationship
Then communicate these effectively to your partner and get feedback
Resolve these issues with your partner (If issues can't be resolved end the relationship)
Psychoanalysis
Delves into unconscious thoughts and childhood experiences to understand current behavior.
"What you resist will persist" - Carl Jung
Steps
1. Explore Unconscious Motives
2. Analyze Childhood Experiences
3. Interpret Symbolic Meanings
Steps Explained
First explore your unconscious behaviors that influence your current behaviors. Unconscious behaviors are behaviors and traits we repress. For more info, understand the shadow's role in the Jungian model.
Next analyze your childhood experiences. There is a lot of evidence supporting that behaviors that get repressed were repressed during our childhood. Freud concluded that these behaviors significantlys influence your current behaviors. Want to change your current behaviors? Figure out what behaviors you repressed when you were young.
Identify your patterns and defense mechanisms. These likely arise from the fear of being vulnerable and not having your needs met. So identify the repressed trait, identify patterns of repression, and identify your defense mechanisms to protect the repressed trait.
Confront these repressed traits. Express your emotions that you have repressed. Be ok with being vulnerable. Let it all out. Confront them and accept them. Accept that you have them and continually reflect on them so you can grow.
Attachment-Based Therapy
Focuses on strengthening the relationship between a child and their primary caregivers.
Steps
1. Explore Attachment History
2. Develop Secure Attachments
3. Improve Relationship Dynamics
Steps Explained
First you have to understand attachment theory developed by John Bowlby. Attatchment Theory states that bonds formed between children and their primary caregivers have profound effects on their emotional and social development.
Next you have to understand your attachment styles. Meaning based on your present relationships how are you attached to them? Is your attachment to them secure, anxious, avoidant, or disorganized?
Then figure out why you have that particular attachment style in the relationship. Identify the behaviors that lead to that attatchment style. If the behavior is tied to a specific trauma you need to work through it to resolve it.
Work on moving away from avoidant attachment styles to secure attatchment styles. You need to be secure in yourself and in your relationships.
Gestalt Therapy
Emphasizes personal responsibility and focuses on the present moment.
Steps
1. Awareness of Here and Now
2. Acceptance of Personal Responsibility
3. Integration of Thoughts, Feelings, and Actions
Steps Explained
First be aware of your present situation within yourself and in your environment. This includes your present Thoughts, Feelings, and Actions. Next accept your responsibilites. Be honest with yourself. You are responsible for your own choices and actions in life. Integrate aspects of yourselves that are suppressed. Accept all parts your experience (suppressed thoughts and emotions).
Existential Therapy
Focuses on free will, self-determination, and the search for meaning.
Steps
1. Explore Life's Meaning
2. Embrace Freedom and Responsibility
3. Confront Anxiety of Existence
Steps Explained
The existential crisis! The realization that the world is absurd and without inherent meaning. That nothing will ever bring you complete statisfaction and the highest values will devalue themselves. How we are all going to die and nobody really knows what is going on. Understand how all these themes impact your life and accept the conditions and limitations of the human experience.
Take responsibility for your decisions and creating your own path in life. Create your own meaning in life: values, goals, passions, beliefs. Create a healthy lifestyle to manage your anxiety that comes from existence.
Strive for authenticity in your interactions and choices. In order to do this you have to be honest with yourself. You have to live based on your truth. You have to learn to be true to yourself and your values.
Group Therapy
Provides therapy in a group setting, fostering support and interaction among participants.
Steps
1. Establish Trust within the Group
2. Share Personal Experiences
3. Develop Coping Skills through Interaction
Steps Explained
Group therapy is usually hosted by support groups like a group dedicated to getting over a drug or being diagnosed with an illness. The group will have meetings and their will be rules to establish trust between all group members. Each individual in the group will share their own personal experiences if they wish and share their support for other members in the group. The goal is to make each other cope better and realize they are not alone in life's challenges.
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy
Focuses on identifying irrational beliefs and changing thought patterns.
Steps
1. Identify Irrational Beliefs
2. Challenge and Dispute These Beliefs
3. Develop Rational Beliefs
Steps Explained
Identify and write down your irrational thoughts and beliefs. Everyone gets irrational beliefs from time to time and you must learn that it's ok. A common one is "I must be perfect" - realisticly this is impossible.
Challenge and dispute these irrational beliefs. This is the hard part. It involves critical thinking skills. When given new evidence and reasoning always be prepared to change your mind.
From doing this over and over and over again - constantly updating your belief system and rationale you wil develop much more rational beliefs/thoughts.
Notice this is different from CBT as it involves rational and irrational beliefs/thoughts rather than negative and positive beliefs/thoughts. Realism and Honesty must be perfomed with both of them however.
This therapy is espically useful in science when irrational and rational beliefs/thoughts are often disputed and it gets uncomfortable due to cognitive dissonance.
Creation

Creation therapy is my favorite type of therapy. There is nothing I love more than seeing the Integration of Music, Drama, Narrative, Art, Movement, Play, and Videos using Jungian and Freudian concepts.
Music Therapy
Music can help us cope with our emotional problems better. By putting on a good song and combining it with one of the Journal/Question Therapies can allow you to challenge your thoughts, beliefs, and values in ways inaccessible without it.
Drama Therapy
Drama can actually be really useful in controlled setting. Being more angry and dramatic can allow you to challenge your thoughts, beliefs, and values more.
Narrative Therapy
Writting out a blog or an essay allows you an easier way to challenge our thoughts, beliefs, and values more. I personally recommend this for everyone. I think it's the best therapy.
Art Therapy
Art is also pretty good too. By creating art, it allows you an easier way to challenge our thoughts, beliefs, and values more.
Movement Therapy
Our bodies are designed to move in general, so movement can really help your psychology. Whether that be dancing, running, or working out - there are signficant mental health benefits to this.
Play Therapy
Playing, Acting, or just having fun in general is great therapy. It's what were designed to do.
Video Therapy
Videos, whether that be recording them or watching them really helps. Again combining Music, Drama, Narrative, Art, Movement, and Play and using the therapies disscussed in Journal/Questions allows you not only to deal with your psychological problems easier but it also creates more subjective value for yourself and everyone around you.
Meditation

Meditation isn't easy, but gets better with practice. Emotional intelligence is an invaluable skill.
Mindfulness Meditation
Involves staying present and being aware of your thoughts and surroundings without judgment. So everytime a thought comes in your head you don't judge it or give any energy to it you just let it be.
Loving-Kindness Meditation (Metta)
Involves sending feelings of love and kindness towards yourself and others. So everytime a thought comes in about someone (no matter who it is) you send love to them.
Body Scan Meditation
Involves paying attention to different parts of your body, noticing any sensations or discomforts. So focusing on your feet and working your way up to your legs, chest, lungs, arms, hands, face, etc.
Mantra Meditation (TM)
Involves repeating a word or phrase silently to focus the mind. This word must not mean anything to you. Like the famous "OM" mantra. When you say it silently nothing should pop in your mind.
Yoga Meditation
Involves combining physical postures, breath control, and meditation. There are many different types of exercises, but the benefits are substantial.
Zen Meditation
Involves sitting in a specific posture and observing the thoughts that pass through your mind without attachment. So not attatching yourself to any thoughts at all.
Vipassana Meditation
Involves focusing on the deep interconnection between mind and body. So focusing on bodily functions like everytime you breath up and down.
Hobby
Animal-Assisted Therapy
Animals never judge us and are always there for us. I love them.
Wilderness Therapy
Forests are super beautiful and interesting. So many different plants, animals, and creatures. They are fun to get lost in.
Growing-Based Therapy
Growing things is a great hobby. You get to take care of it and fruit the rewards when its ready. Plus its healthy!
Therapeutic Video Games
Playing video games (I mean the good ones - not the hyper addictive ones) can actually be really nice. Same is true with watching shows or reading stories.
Puzzle-Based Therapy
Whether it is engineering or coding or just trying to solve a mystery in life. The process can be really psychologically rewarding if it is done right.
Engineered

Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy
Uses psychedelic substances in a therapeutic setting to enhance the process of self-exploration and healing.
Steps
1. Screening and Preparation
2. Guided Psychedelic Experience
3. Integration Sessions
Steps Explained
This one of the most exciting and dangerous. It involves getting a trip sitter and taking a low dose of psilocybin and having the trip sitter watch you in a calm relaxed environment. In a clinical setting they enchance this by making the patient where headphones, wear a blindfold and make sure someone is in the room always watching them. The psychological benefits of these trips are quite insane and still being researched. However, there are still a lot of mysteries and potential side effects so researchers are still proceeding with caution.
Biofeedback
Uses electronic monitoring to train individuals to gain control over involuntary bodily functions.
Steps
1. Measure Physiological Responses
2. Provide Real-time Feedback
3. Practice and Develop Control Over Responses
Steps Explained
Biofeedback is another very exciting and interesting therapy along with Psychdelic Therapy. It involves using technology (non-invasive) or (invasive) to improve psychological feelings. It should be interesting to see how biofeedback affects us as technology improves
Hypnotherapy
Employs guided relaxation and intense concentration to achieve a heightened state of awareness, often referred to as a trance.
Steps
1. Induction of Hypnotic State
2. Therapeutic Suggestions or Explorations
3. Gradual Emergence from the Hypnotic State
Steps Explained
In Hypnotherapy there is a guider and a follower. The guider employs various methods to get the follower in various hynoptic states.
Resources
The Integral Guide To Well Being
Mental Health Resources
Illusions
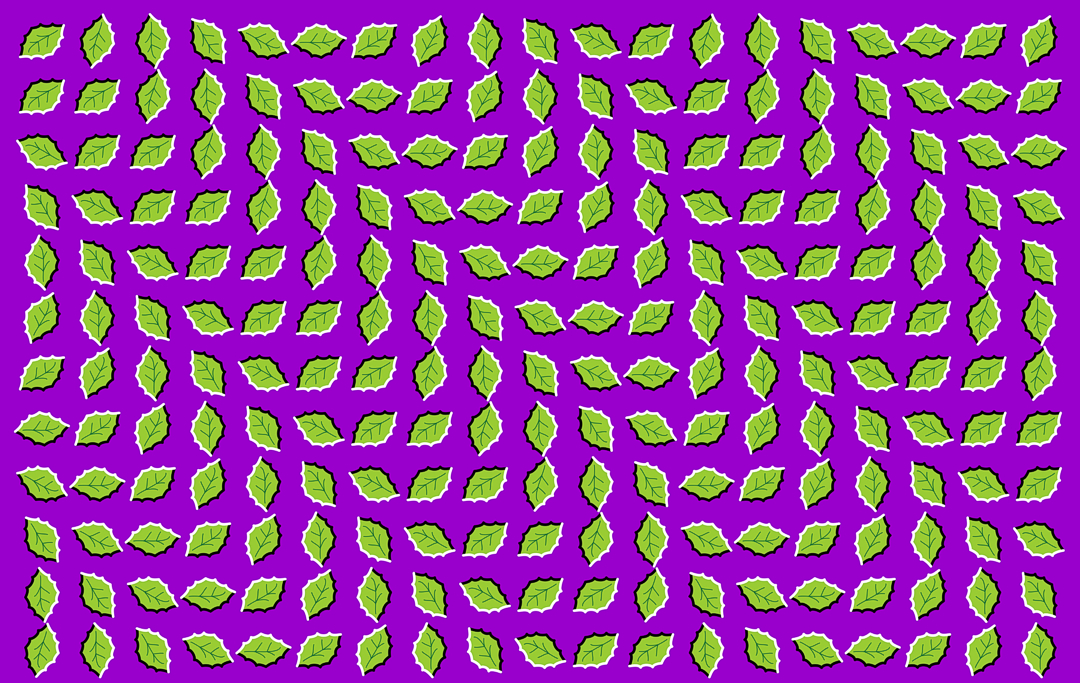
We don't perceive reality correctly. We perceive a cherry picked version of reality that only exists because it allowed us to survive and to reproduce. We have evolved many sensory organs to help help us perceive reality. These include our visual (sight), auditory (hear), olfactory (smell), gustatory (taste), and tactile (touch) senses. The failure of these perception systems is called illusions.
Illusions are a complete failure of our perception systems, but it doesn't mean the reality we're seeing isn't necessarily wrong or right, as there is no such thing. It is merely the boundaries of what our interface is capable of, what our operating system can handle. The mere fact that we have an interface at all, is what amazes me more than anything. Maybe it's the only way we can truly experience reality, and that is certainly a humbling thought.
Visual illusions are the failure of visual perceptions. That image you see above is my favorite one, and if you want to learn more keep scrolling or check out Akiyoshi's illusions pages . Feel free to explore as many visual illusions as you would like to whether that be motion, color, distance, alignment, shadow, size, and direction.
Table of Contents
Motion
Perpheral Drift Illusion
Motion After Effects
Color
Fechner Color
White's Illusion
Troxler's Fading
Afterimage
Distance
Munker illusion
Alignment
Cafe Wall Illusion
Shadow
Kinetic Depth Effect
Grid Illusion
Size
Ebbinghaus Illusion
Müller-Lyer Illusion
Ponzo Illusion
Shepard Tables
Direction
Anamorphosis
Cool Illusion Websites
Motion
Perpheral Drift Illusion
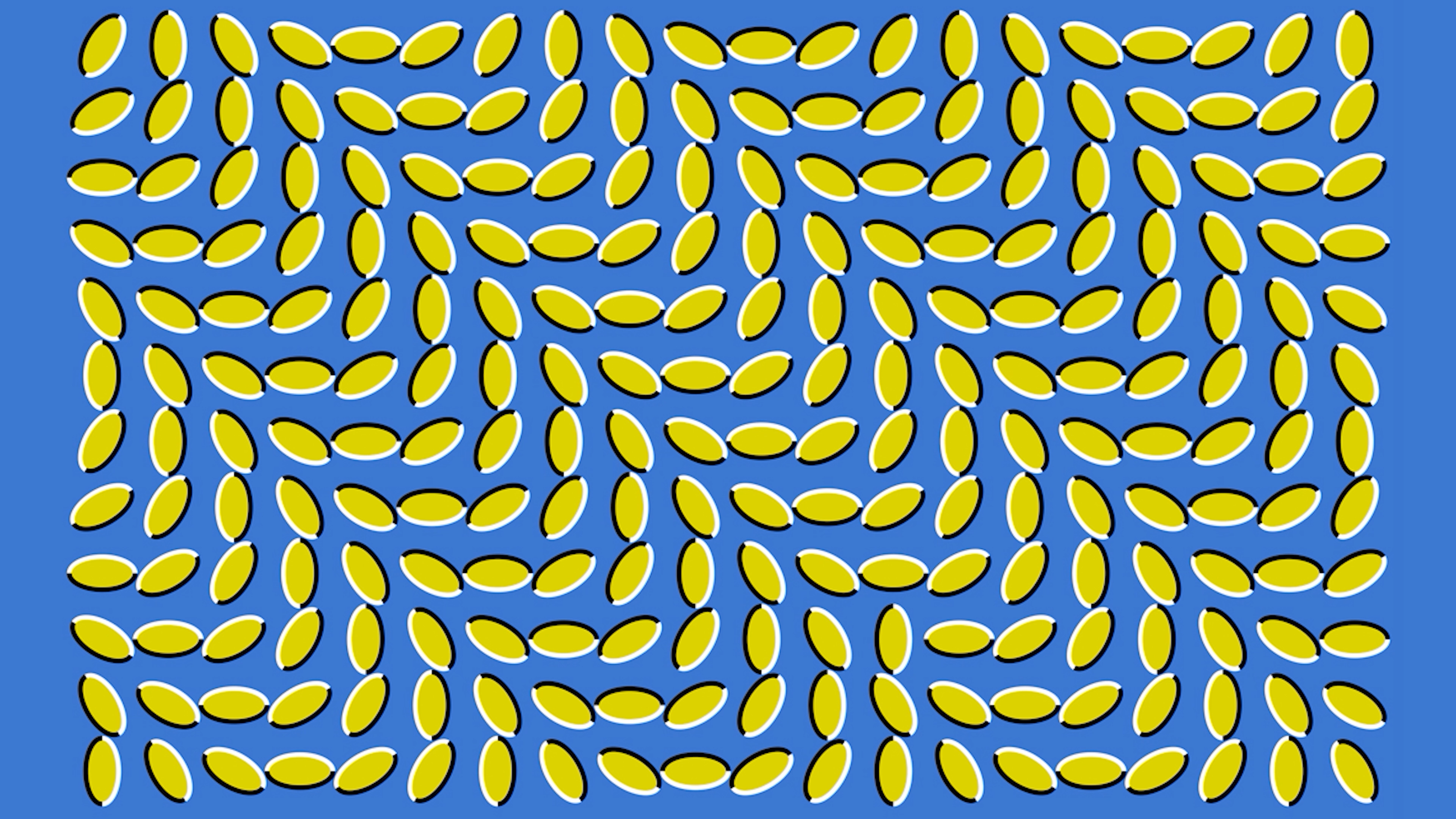
This illusion will make it appear like the green ovals are moving somehow when they are really not. You see, our neurons are adapted to perceive lightness & darkness differently, and when we combine we get strange results.
When you see a dark square your visual neurons should fire out. When you see a light square your visual neurons should fire in. When we take a square and make half of it dark & half of it light your neurons should fire towards the darkness. So if you can quickly place a shape that fires neurons UP next to a shape that fires neurons DOWN, as you look across it you can be able to perceive motion despite motion not being present.
Using this principle we can make your neurons perceive false movement. This is called the Peripheral Drift illusion. The famous rotating snakes uses this prinicple and keeps your neurons firing in a circle. For more check out Akiyoshi's Rotational illusions
Motion After Effects
Stare at the center of the black circle for 30+ seconds or so and then look away really quickly at something close up. You should be perceiving motion on a stationary object
This happens because your brain's motion-detecting neurons get used to the spinning motion. When you look away at something still, these neurons need a moment to adjust. During this adjustment, they briefly send signals as if whatever you're looking at is moving, but in the opposite direction.
Color
Contrast effect
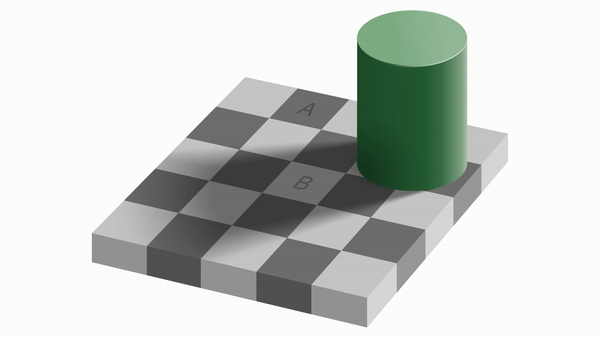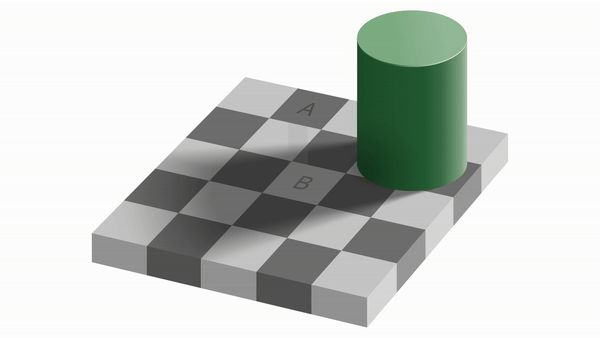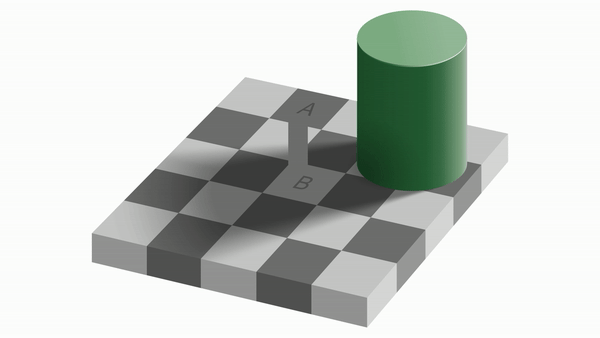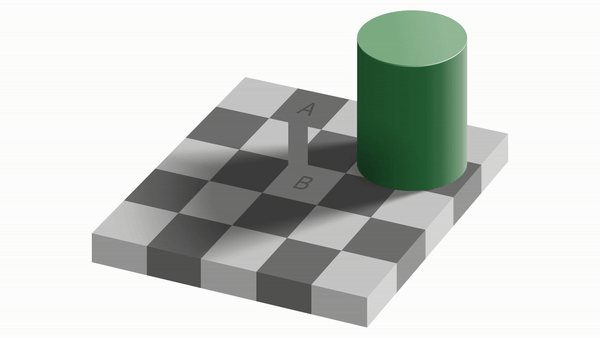
A and B look like they are different colors even though they are the same color! This is because our visual neurons perceive the same color differently near darkness and lightness.
Troxler's Fading
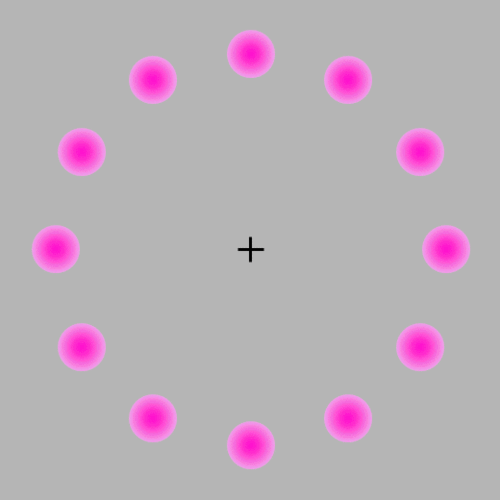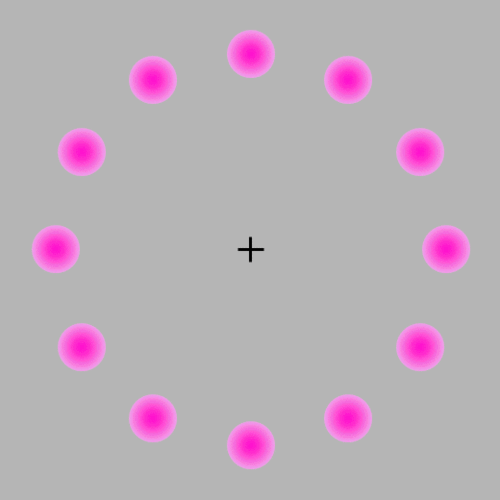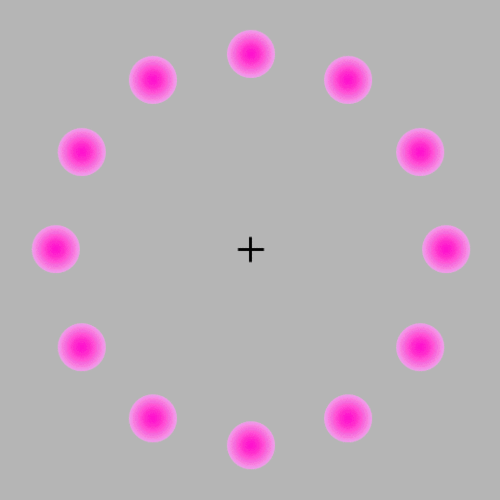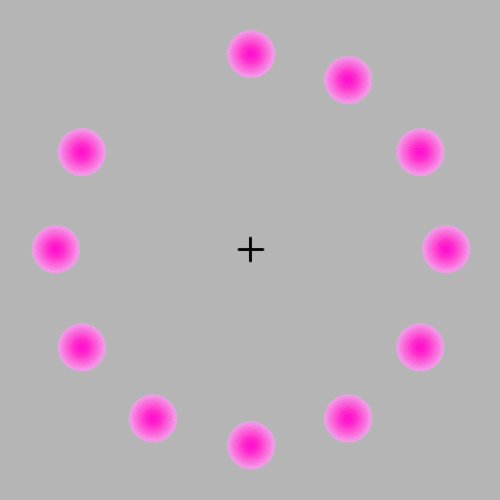
If you focus on the center the pink circles should appear to fade away even though they are not fading away they are simply disappearing. I also see green in the fade away effect even though there is no green.
As for why this happens, the hypothesis is, when fixating on a single point, the brain might reduce the neural signals associated with the unchanging stimuli in the periphery, leading to their fading from conscious awarenes
Afterimage

Stare at the black dot in the center. After 30 seconds or so the image will change to black and white. You will perceive color just for a couple seconds within the image despite the image being entirely black and white.
When you stare at a brightly colored image the photoreceptor cells in your eyes become fatigued to the specific wavelengths of light present in that image. As a result, when you shift your gaze to a neutral background, the less fatigued receptors become more active, generating an afterimage in colors opposite to those in the original image.
Distance
Munker illusion

When the circles are farther away, they will appear red, blue, and green. However, when zoomed in they can be seen as all the same color.
At a distance, your eyes perceive the overall color of a region rather than individual details. The colored lines blend and mix, leading to a perceived color for each circle that is different from the actual colors of the lines. When you zoom in, your eyes can distinguish the individual colors of the lines more clearly.
Alignment
Cafe Wall Illusion
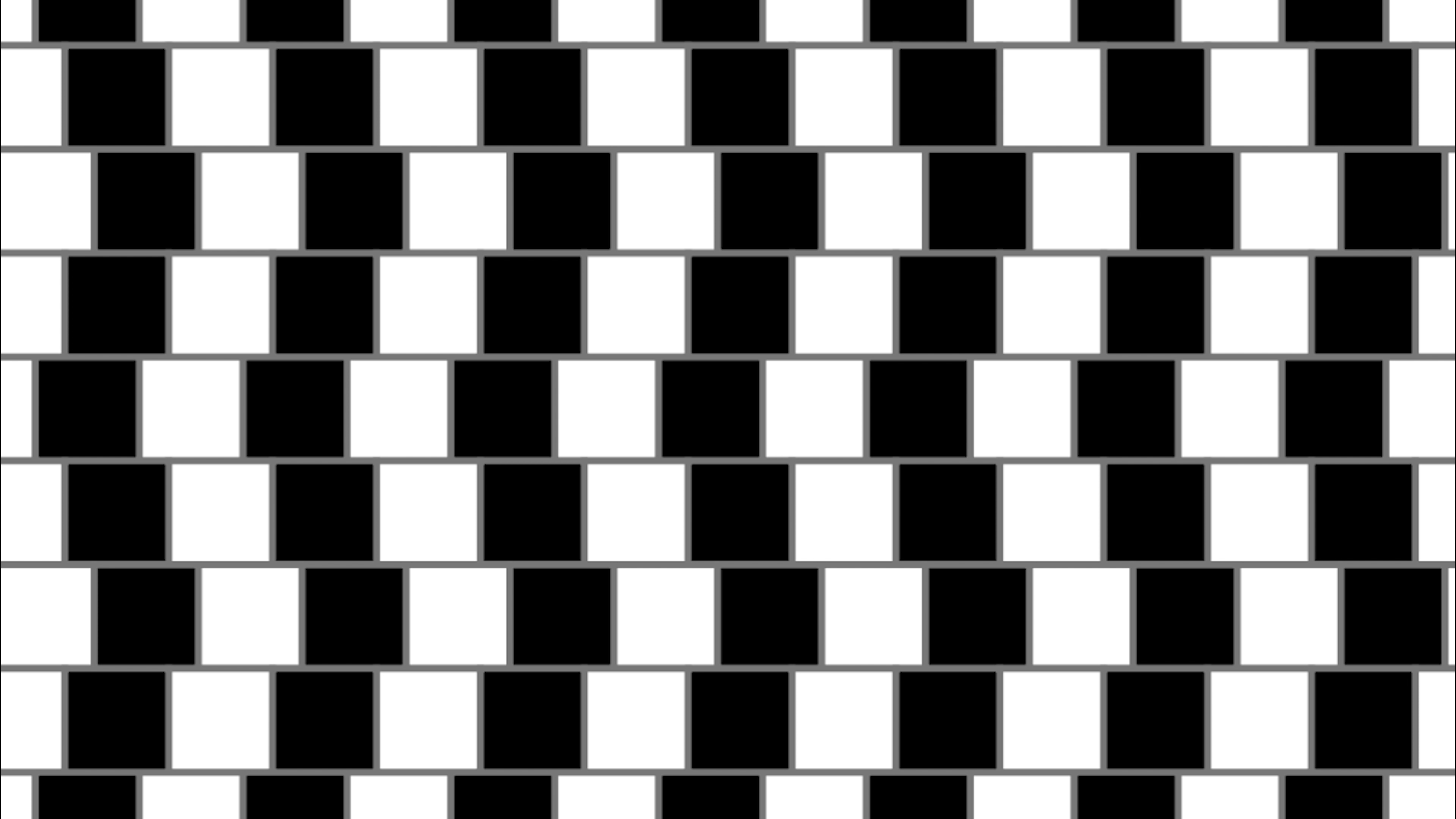
These seemingly parallel lines appear to be sloped or moving down and up due to light and dark squares offsetting each other. Light & Dark offsets can make us perceive a straight parallel to be misaligned.
Shadow
Kinetic Depth Effect

Is the women is spinning clockwise or counterclockwise? What if I told you it can be percieved as both.
Basically you can percieve her standing leg to be infront of her moving left or vice versa which causes you to percieve her to spin a different way.
Our brain makes a guess because it has to. It needs to make out the object even though it doesn't have all the details.
Grid Illusion
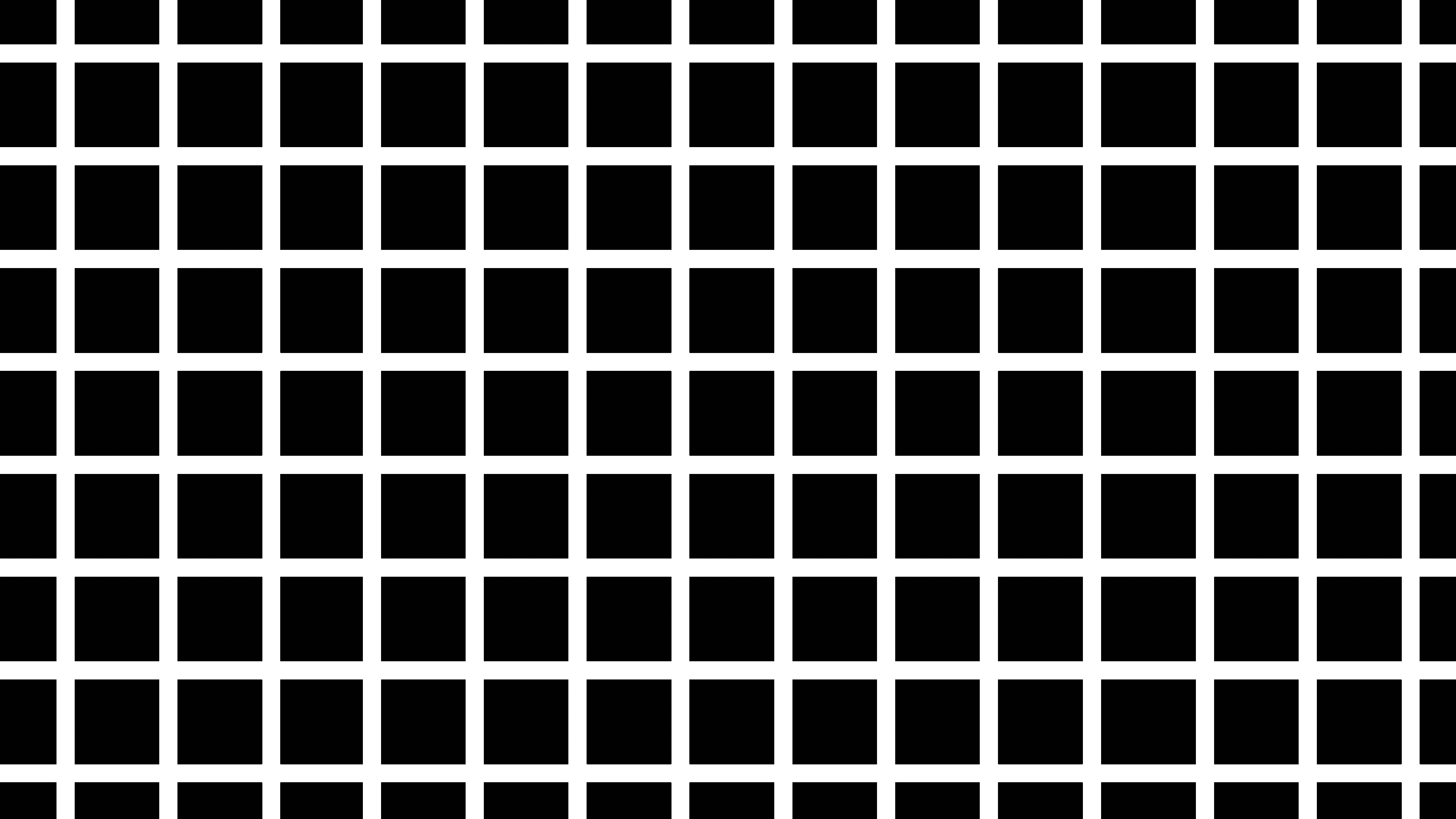
Do you percieve dark shadows within the intersections of the grid despite there not being any? If you fixate on one white intersection the dark shadows will disappear. How mysterious!
Lateral inhibition is when one neuron signals to its neighbors to "quiet down" when it's active. This mechanism enhances the contrast between light and dark areas, helping us perceive edges and boundaries more clearly. When you focus on the grid, the neurons at the intersections actively inhibit their neighbors, making the black areas darker and the white lines even brighter. However, when you look directly at an intersection, the effect is reduced, and the illusion of black dots diminishes. The brain processes these signals, and the heightened contrast due to lateral inhibition creates the perception of dark dots where there are none.
Size
Ebbinghaus Illusion
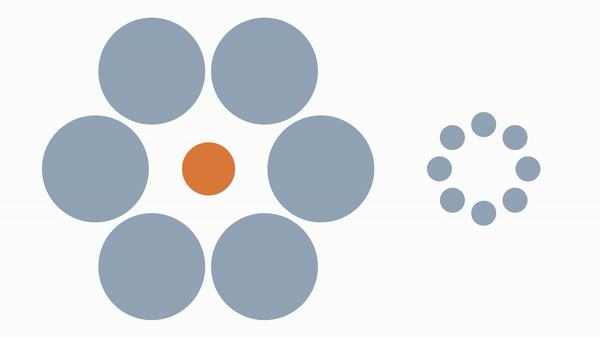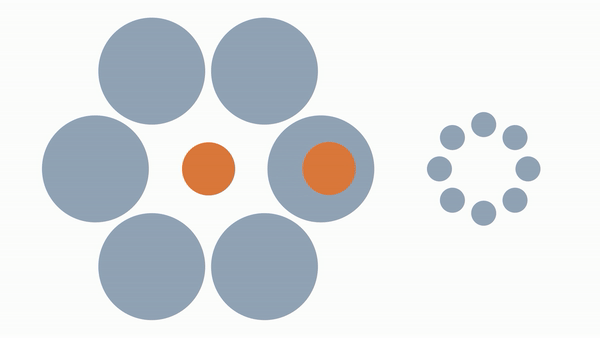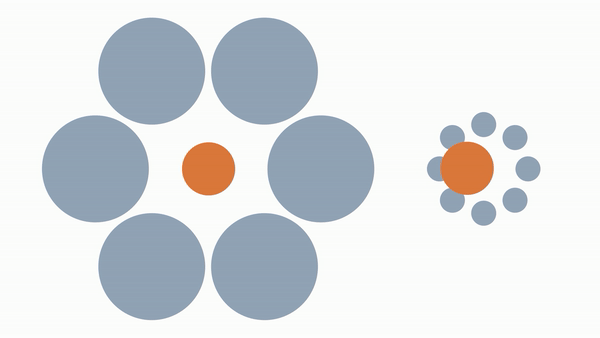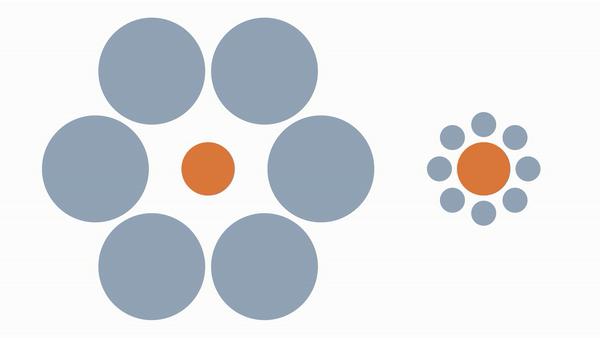
When you place the same sized circle around larger/smaller objects it appears larger/smaller than it really is despite it being the same size.
Our neurons that percieve size make assumptions/adjustments about an object's size when its surrounded by larger/smaller objects.
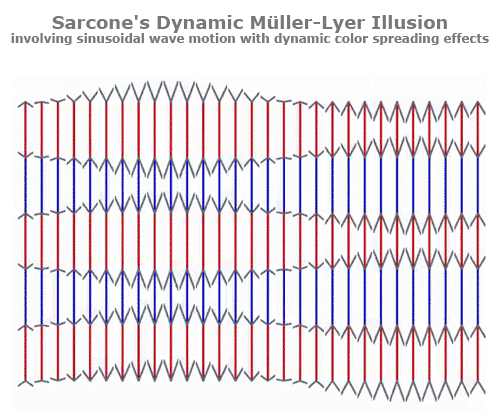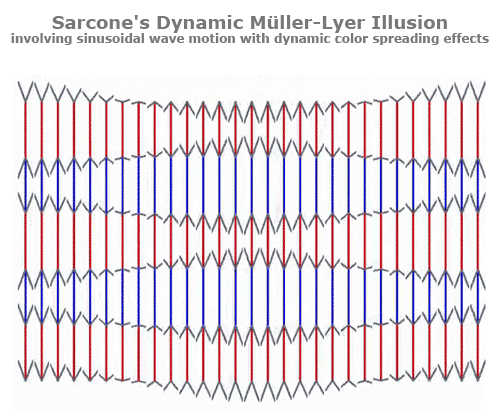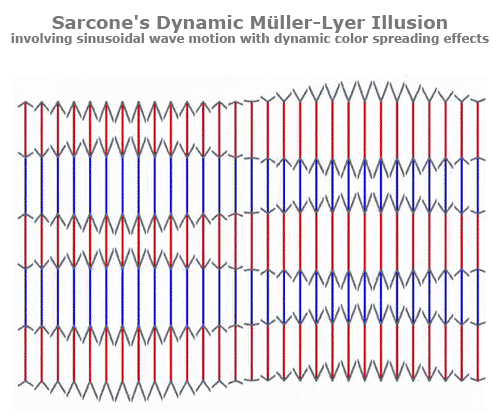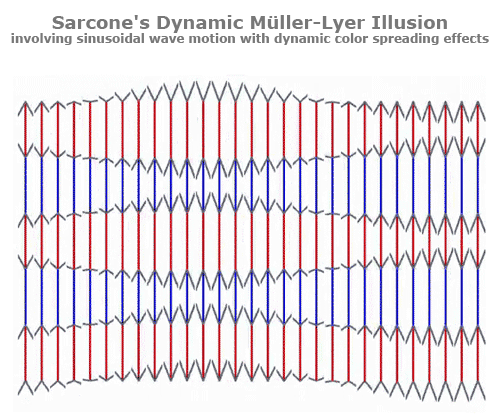
Müller-Lyer Illusion
The line between the arrows appears shorter than the line between the tails. However, they are actually the same size in length.
Your brain ignores the distance at the head of the arrow making the head appear shorter, while the tail appears longer.
Ponzo Illusion
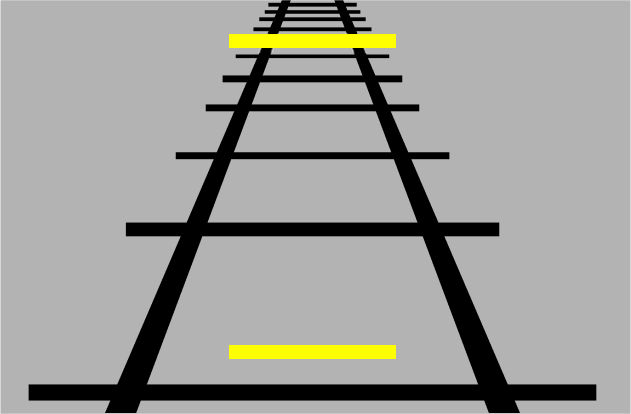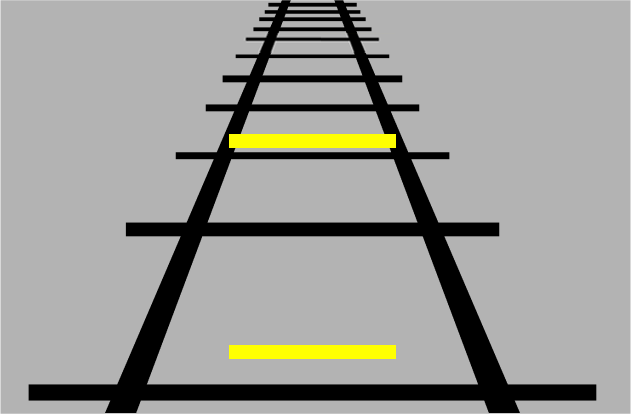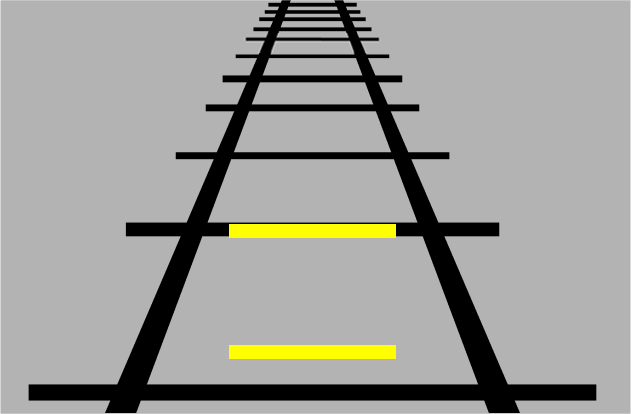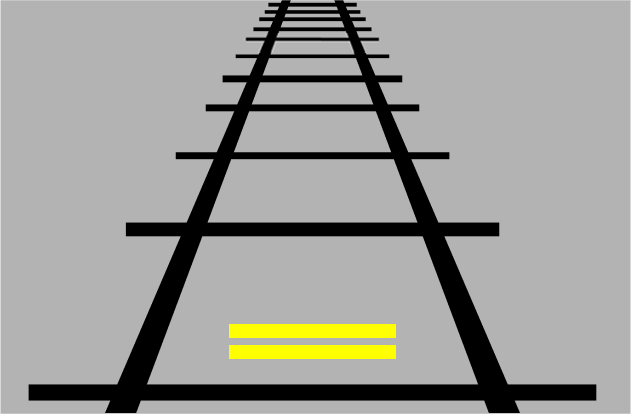
The yellow bar at the top appears longer than the yellow bar at the bottom despite them being the same length due to converging lines.
Your brain relies of depth perception to tell it how large and small objects are, however if we keep an object the same size and put it at a different depth we can fool it.
Shepard Tables
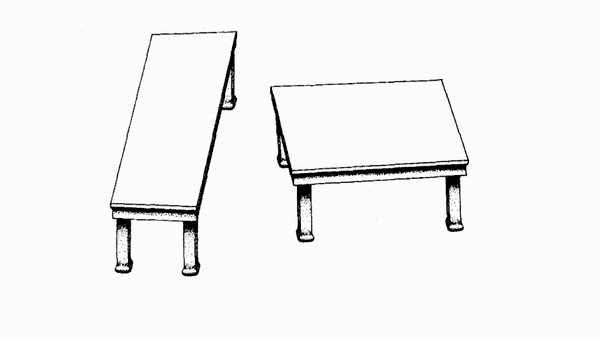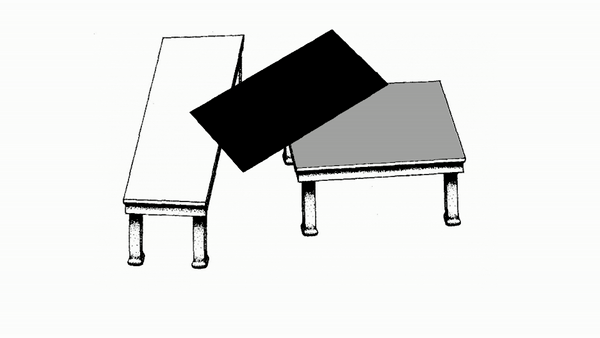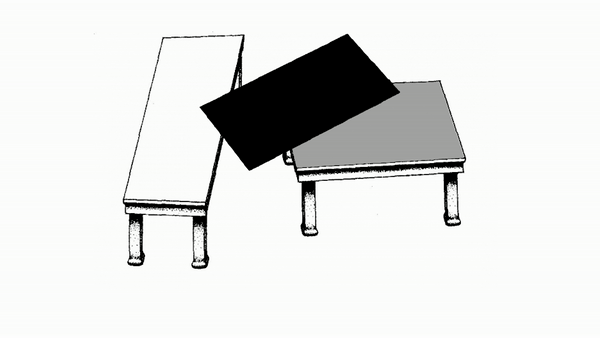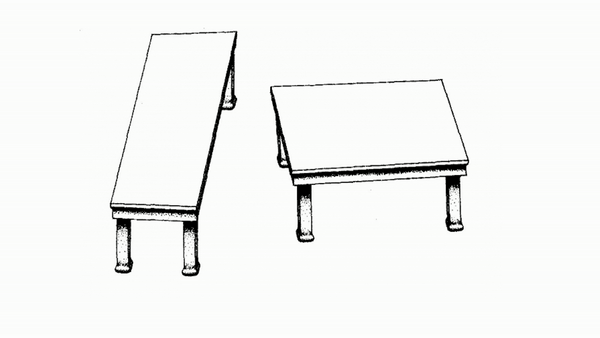
The Table tops of the two tables appear to be different sizes when they are actually the same size.
Your brain makes assumptions about how similar objects are based on size, shape, however a parallelogram throws a curve ball at your brain. It's able to look different just enough for your brain to not be able to tell the difference.
Direction
Anamorphosis
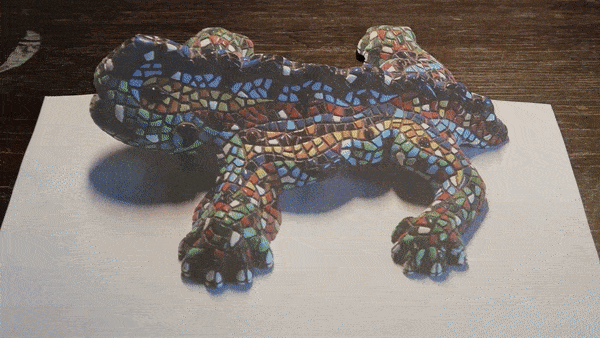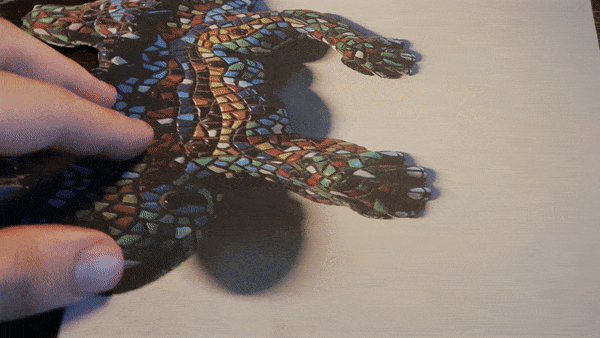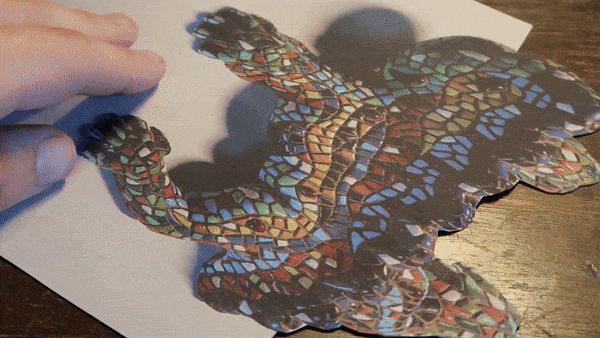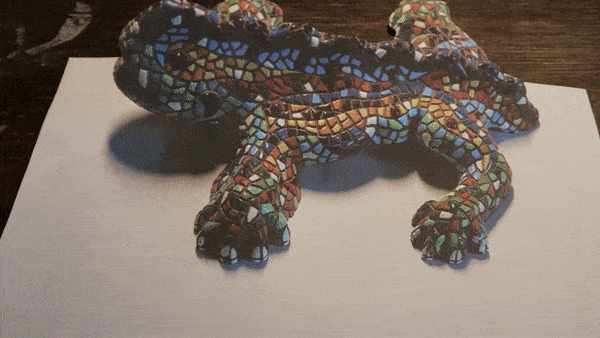
Does this lizard appear real to you? Like an actual 3D object?! Well it's not! It's a printed out lizard on 2D paper! Muahahahaha!
When we view an anamorphic image from the designated angle our brain corrects the distortion, reconstructing the intended image. This correction happens because our visual system is trained to make sense of the world by interpreting spatial relationships, depth cues, and perspective. Anamorphic images exploit these processes by presenting distorted information that our brains can reconfigure into a recognizable and undistorted form when viewed from the intended viewpoint.
Cool Illusion Websites
Akiyoshi's illusion pages
Journal of illusion
152 Visual Phenomena & Optical Illusions with explanations
David Novick's illusions
Anopticalillusion
Biases
Emotions
Speed
Info-overload
Ambiguity
BASIC PSYCH GUIDE
Techniques For Learning
Useful learning strategies
"The biggest communication problem is we do not listen to understand. We listen to reply,” - Stephen Covey
Iceberg Model
First Priniciples
Concept Map
Issue Trees
Socratic Method
CHATGPT (USE AI AS A LEARNING TOOL)
Useful Models
Maslows Hierachy of Needs
Cognitive Bias Codex
Freud Iceberg Ego Model
Carl Jung's Model of the Psyche
Brain Model
Habit Loop
Operant Conditioning
Cognitive Development
Psychosocial Development
Proximal Development
Psychosexual Development
Moral Development
Attachment Theory
Social Learning Theory
The Big Five Personality Traits
Multiple Intelligences
Five Laws of Stupidity
Basic Fundamentals
Introductory Psychology
Theories of Psychology
Psychoanalytic Theory
Behaviorism
Humanistic Theory
Cognitive Theory
Biological Theory
Evolutionary Theory
Sociocultural Theory
Systems Theory
Branches of Psychology
Clinical Psychology
Cognitive Psychology
Developmental Psychology
Biological Psychology
Social Psychology
Evolutionary Psychology
Behavioral Psychology
Psychodynamic Psychology
Abnormal Psychology
Forensic Psychology
Health Psychology
Humanistic Psychology
Personality Psychology
History of Psychology
Ancient Times
Ebers Papyrus
Socrates
Plato
Aristotle
Middle Ages To Renaissance
Al-Razi
Avicenna
St. Augustine
St. Thomas Aquinas
René Descartes
1800s-1900s
Wilhelm Wundt
Edward Titchener
Charles Darwin
Sigmund Freud
Carl Jung
John B. Watson
B.F. Skinner
1900s-2000s
Max Wertheimer
Kurt Koffka
Wolfgang Köhler
Carl Rogers
John Bowlby
Abraham Maslow
Jean Piaget
Noam Chomsky
Martin Seligman
Research Methods in Psychology
Experimental Design
Quantitative and Qualitative Research
Ethics in Psychological Research
Biological Psychology
Neuroscience
Neurons
Synaptic Transmission
Neurotransmitters
Brain Imaging Techniques (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG)
Neuroplasticity
Memory
Sensation and Perception
Transduction
Threshold
Sensory Systems
vision
hearing
touch
taste
smell
Gestalt Principles
Perceptual Constancies
shape
size
color
distance
motion
direction
shadow
Perceptual Adaptation
Attention
Sensory Adaptation
Signal Detection Theory
Bottom-Up vs. Top-Down Processing
Areas of The Brain
Cerebellum
Frontal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Brainstem
Sleep
Stages of Sleep
Functions of Sleep
Circadian Rhythms
Sleep Disorders
Effects of Sleep Deprivation
Dreams
Hormones and Behavior
Endocrine System Basics
Hormonal Influence on Behavior
Testosterone and Estrogen
Oxytocin
Cortisol
Hormones influence on Mental Health
Developmental Role of Hormones
Hormonal Treatments
Sleep Hormones
Melatonin
Chemicals Influence on Hormones
Psychopharmacology
Antidepressants
Anxiolytics
Antipsychotics
Mood Stabilizers
Stimulants
Sedative-Hypnotics
Developmental Psychology
Child Development
Theories of Child Development
Cognitive
Psychosocial
Sociocultural
Attachment
Physical
Language
Social
Emotional
Moral
Nature vs. Nurture
Adolescent Development
Puberty
Sexuality
Adult Development and Aging
Physical
Cognitive
Cognitive Psychology
Memory
Types of Memory
Sensory Memory
Short-term Memory (STM)
Long-term Memory (LTM)
Processes of Memory
Encoding
Storage
Retrieval
Long-term Memory
Explicit (Declarative) Memory
Implicit (Non-declarative) Memory
Factors Affecting Memory
Forgetting
Memory Biases
Conformation Bias
Source Amnesia
Misinformation Effect
Brain Structures Involved in Memory
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Cerebral Cortex
Basal Ganglia
Memory Disorders
Amnesia
Alzheimer's
Korsakoff's Syndrome
Déjà vu
Attention
Types of Attention
Selective Attention
Divided Attention
Sustained Attention
Shifting Attention
Attentional Capacity
Factors Influencing Attention
Salience
Emotion
Motivation
Fatigue
Neuroscience of Attention
Frontal and Parietal Lobes
Thalamus
Reticular Activating System
Neurotransmitters
Attentional Disorders
ADHD
Cognitive Load
How Modern Technology Affects Attention Spans
Decision Making and Problem Solving
Types of Decision-Making
Problem-Solving Strategies
Barriers to Effective Problem-Solving
Role of Emotions
Neuroscience of Decision-Making
Prefrontal Cortex
Amygdala
Basal Ganglia
Cognitive Biases and Heuristics
Common Biases
Conformation Bias
Dunning Kruger Effect
Cognitive Dissonance
Gas-lighting
Virtue Signaling
Common Heuristics
Availability Heuristic
Types of Biases
Emotional Biases
Speed Biases
Ambiguity Biases
Information Biases
Memory Biases
Social Biases
Group Biases
Egocentric Biases
Understand Why We Have Biases
Understand Neuroscience of Biases
Understand Biases Roles in Decisions, Conflicts, and in History
Understand How To Overcome Biases
Perception and Illusions
Understand That we do not percieve everything there is to percieve
Understand Why we have flawed perception systems
Understand How Illusions relate to our senses
Types of Illusions
Optical Illusions (Visual)
Auditory Illusions (Hearing)
Tactile Illusions (Touch)
Multimodal Illusions (Multiple Senses)
Understand Role of Brain in perception systems and its limitations
Gestalt Principles
Perceptual Constancies
shape
size
color
distance
motion
direction
shadow
Behavioral Psychology
Classical Conditioning
Unconditioned Stimulus
Unconditioned Response
Conditioned Stimulus
Conditioned Response
Operant Conditioning
Positive & Negative Reinforcements
Positive & Negative Punishments
Observational Learning
Habit Formation and Habit Loops
cue (trigger)
routine (behavior)
reward
Behavior Modification
Social Psychology
Group Dynamics
Group Biases
In-Group
Out-Group
Groupthink
Riots
Heard behavior
Cults
Group Formation
Group Roles
Group Leaders
Us vs. Them Mentality
Political Group Behavior
Obedience to Authority
Social Media Groups
4chan
Social Influence
Conformity
Compliance
Obedience
Social Facilitation
Social Loafing
Interpersonal Relationships
Understand why people form relationships
Understand why relationships fail
Understand relationship skills
Assortment effect
Attatchment Styles
Secure
Avoidant
Anxious
Communication
Values
Attraction
Attrative vs Unattractive Behavior
Varies from culture to culture
Similarities & Differences in Attraction For Men & Women
Nature (Best Traits Possible) vs Nurture (Cares About Me & My Offspring)
Investment Model
Investment Paradox
Vulnerability
Vulnerability is how we form emotional connections
Polarization
External Influences
social status
financial resources
physical appearance
Trust and Commitment
Relationship Satisfaction
Social Exchange Theory
Equity Theory
Psychodynamic Psychology
The Unconscious
Implicit Biases
Neuroscience
Free Association
Tourette's Syndrome
Dream Analysis
Ego, Superego, and Id
Id (unconscious) (primial)
Ego (conscious) (unconscious) (rational)
Superego (conscious) (unconscious) (moral)
Defense Mechanisms
Purpose of Defense Mechanisms
Primary Defense Mechanisms
Repression
Denial
Projection
Displacement
Regression
Sublimation
Rationalization
Reaction Formation
Intellectualization
Identification
Jungian Concepts
Collective Unconscious
Archetypes
Hero
Villian
Wise
Wicked
Shadow
Anima and Animus
Self
Individuation
Synchronicity
Active Imagination
Abnormal Psychology
Mood Disorders
Types
Depression
Bipolar
Symptoms
Causes
Diagnosis
Treatments
Prevention
Anxiety Disorders
Types
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Panic Disorder
Phobias
Social Anxiety Disorder
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Symptoms
Causes
Diagnosis
Treatments
Prevention
Psychotic Disorders
Types
Schizophrenia
Symptoms
Hallucinations
Delusions
Causes
Diagnosis
Treatments
Prevention
Personality Disorders
Types
Paranoid Personality Disorder
Schizoid Personality Disorder
Schizotypal Personality Disorder
Antisocial Personality Disorder
Borderline Personality Disorder
Histrionic Personality Disorder
Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Avoidant Personality Disorder
Dependent Personality Disorder
Symptoms
Causes
Diagnosis
Treatments
Prevention
Childhood Disorders
Types
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Learning Disorders (dyslexia) (dyscalculia) (dysgraphia)
Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)
Symptoms
Causes
Diagnosis
Treatments
Prevention
Cognitive Disorders
Types
Delirium
Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI)
Dementia
Symptoms
Causes
Diagnosis
Treatments
Prevention
Treatment and Therapy
Theoretical Orientations
Therapeutic Techniques
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Interpersonal Therapy (IPT)
Exposure Therapy
Psychoanalysis
Pharmacotherapy
Clinical Psychology
Assessment and Diagnosis
Psychometric Testing
Clinical Interviews
Diagnosis
Clinical Neuropsychology
Brain-Behavior Relationship
Neuropsychological Testing
Neurological Disorders
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Core Principles
Techniques
Applications
Psychodynamic Therapy
Freudian Concepts
Transference and Countertransference
Interpretation
Humanistic Therapy
Client-Centered Therapy
Existential Therapy
Gestalt Therapy
Group Therapy, Family Therapy
Dynamics
Systems Theory
Expressive Therapies
Art Theory
Music Theory
Drama Theory
Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy
Mechanisms
Safety and Precautions
Integration
Evolutionary Psychology
Adaptations
Environment of Evolutionary Adaptedness (EEA)
Reproductive Success
Sexual Selection
Parental Investment
Mate Preferences
Evolutionary Perspective on Behavior
Innate Behaviors
Mismatches with Modern Society
Forensic Psychology
Criminal Profiling
Behavioral Evidence Analysis
Limitations
Role in Investigations
Legal and Court Psychology
Expert Witness
Competency Evaluations
Child Custody Evaluations
Consultation
Rehabilitation and Treatment Recommendations
Psychological Assessment in the Legal System
Risk Assessments
Mental State Examinations
Malingering Evaluations
Neuropsychological Assessments
Assessments for Specific Legal Criteria
Health Psychology
Stress, Coping, and Health
Stress
Sources of Stress
Effects on Health
Coping Mechanisms
Health Behavior Change
Health Belief Model
Stages of Change Model
Promotion of Healthy Behaviors
Pain Management
Types of Pain
Cognitive-Behavioral Approaches
Pharmacological Treatments
Psychological Impact
Personality Psychology
Personality Theories
Five Factor Model (Big Five)
Eysenck's PEN Model
Social-Cognitive Theories
Behavioral Theories
Personality Assessment
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
NEO-PI-R
16 Personality Factors (16PF)
Rorschach Inkblot Test
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
Self-Report Questionnaires
Behavioral Observations
Interviews
Humanistic Psychology
Self-actualization
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Basic Structure
Different Needs For Survival
Progression
Carl Rogers' Person-Centered Theory
Core Conditions for Growth
Self-concept
Educational Psychology
Learning Theories and Instruction
Information Processing
Constructivism (Piaget)
Understand different types of learning models
Understand everyone learns differently
Motivation in Education
Internal vs External
Expectancy-Value Theory
Self-Determination Theory
Child and Adolescent Development in School Contexts
Child Development
Emotion Psychology
Biological and Cognitive Aspects of Emotion
Theories of Motivation
Cross-Cultural Psychology
Cultural Variations in Behavior and Mental Processes
Acculturation and Identity
Exercise Psychology
Motivation in Sports & Video Games
Performance Enhancement
Psychological Benefits of Exercise
Psychological Benefits of Video Games
Environmental Psychology
Human-Environment Interactions
Environmental Stressors and Well-being
Design and Environmental Aesthetics
Industrial-Organizational Psychology
Workplace Behavior
Human Factors
Organizational Culture
Research Psychology
Research Methods
Experimental Designs
Correlational Designs
Observational Studies
Surveys and Questionnaires
Longitudinal vs. Cross-Sectional Studies
Case Studies
Ethical Considerations
Statistical Analysis
mean
median
mode
standard deviation
significance testing
regression
ANOVA
factor analysis
Research Tools And Software
Qualtrics (Surveys)
JASP (Statistics)
SPSS (Statistical Analysis)
R and RStudio (Statistics)
Morae (Testing)
Jupyter Notebook (Data Analysis)
Prolific (Participant Recruitment)
SONA Systems (Participant Management)
Interpreting Results
Dissemination
Graduate Jobs
Clinical Psychologist
Counseling Psychologist
Educational Psychologist
Health Psychologist
Forensic Psychologist
Neuropsychologist
Industrial-Organizational
Human Resources Officer
Psychotherapist
General University Curriculum
General Psychology
Statistics in Psychology
Research Methods
Biological Psychology
Developmental Psychology
Cognitive Psychology
Abnormal Psychology
Social Psychology
Personality Psychology
Industrial-Organizational Psychology
Psychological Testing and Measurement
Books
Remember, you don't have to actually buy them - only focus on the information you need for the area you're going into (use the iceberg model in combination with first principles). You can always copy and paste pdf text into chatgpt and use it for basic summaries if you need help
Introductory Psychology
Developmental Psychology
Social Psychology
Biological Psychology
Neuroscience
Abnormal Psychology
Cognitive Psychology
Clinical Psychology
Psychoanalysis
Freud
Jung
Health Psychology
Industrial-Organizational Psychology
Evolutionary Psychology
Behavioral Psychology
Consciousness and Spirituality
Research Psychology
Online Resources
Psyarxiv (GET USE TO READING RESEARCH PAPERS)
American Psychological Association (APA)
Academia
PsycNET
PubMed
Researcher (app)
Google Scholar
Coursera
Society for Personality and Social Personality
Society for Industrial ad Organizational Psychology
PsychCentral
Simple Psychology
PsyPost
British Psychological Society
TakingTheEscalator
MindHacks
thelastpsychiatrist
SPSS
JASP
R and RStudio
Qualtrics
Prolific
SONA Systems
Jupyter Notebook
Morae
edX
MIT Opencourseware
Open Yale Courses
Khan Academy (MCAT)
FutureLearn
Udemy
Udacity
The Great Courses
Alison
Social Science Research Network (SSN)